T2 Mapping - Multi-echo SE#
T2 mapping using a multi-echo spin echo sequence where a single readout line is acquired. A long repetition time (TR) is used to ensure full signal recovery before the next k-space line is acquired.
Imports#
import tempfile
from pathlib import Path
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import MRzeroCore as mr0
import numpy as np
import torch
from cmap import Colormap
from einops import rearrange
from mrpro.algorithms.reconstruction import DirectReconstruction
from mrpro.data import KData
from mrpro.data import SpatialDimension
from mrpro.data.traj_calculators import KTrajectoryCartesian
from mrpro.operators import DictionaryMatchOp
from mrpro.operators.models import MonoExponentialDecay
from mrseq.scripts.t2_multi_echo_se_single_line import main as create_seq
from mrseq.utils import sys_defaults
Settings#
We are going to use a numerical phantom with a matrix size of 128 x 128. The repetition time is set to 20 seconds to ensure also tissue with long T1 such as CSF is fully relaxed.
image_matrix_size = [128, 128]
repetition_time = 20
tmp = tempfile.TemporaryDirectory()
fname_mrd = Path(tmp.name) / 't2.mrd'
Create the digital phantom#
We use the standard Brainweb phantom from MRzero, but we set the B1-field to be constant everywhere.
phantom = mr0.util.load_phantom(image_matrix_size)
phantom.B1[:] = 1.0
Create the multi-echo SE sequence#
To create the multi-echo SE sequence, we use the previously imported t2_multi_echo_se_single_line script.
sequence, fname_seq = create_seq(
system=sys_defaults,
test_report=False,
timing_check=False,
fov_xy=float(phantom.size.numpy()[0]),
tr=repetition_time,
n_readout=image_matrix_size[0],
n_phase_encoding=image_matrix_size[1],
)
Saving sequence file 't2_multi_echo_se_single_line_200fov_128nx_128ny_5TEs.seq' into folder '/home/runner/work/mrseq/mrseq/examples/output'.

Simulate the sequence#
Now, we pass the sequence and the phantom to the MRzero simulation and save the simulated signal as an (ISMR)MRD file.
mr0_sequence = mr0.Sequence.import_file(str(fname_seq.with_suffix('.seq')))
signal, ktraj_adc = mr0.util.simulate(mr0_sequence, phantom, accuracy=1e-5)
mr0.sig_to_mrd(fname_mrd, signal, sequence)
>>>> Rust - compute_graph(...) >>>
Converting Python -> Rust: 0.007875642 s
Compute Graph
Computing Graph: 0.008967433 s
Analyze Graph
Analyzing Graph: 0.000160623 s
Converting Rust -> Python: 0.001881939 s
<<<< Rust <<<<
/opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.12.12/x64/lib/python3.12/site-packages/pypulseq/Sequence/sequence.py:863: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in divide
gw_pp.append(PPoly(np.stack((np.diff(gw[1]) / np.diff(gw[0]), gw[1][:-1])), gw[0], extrapolate=True))
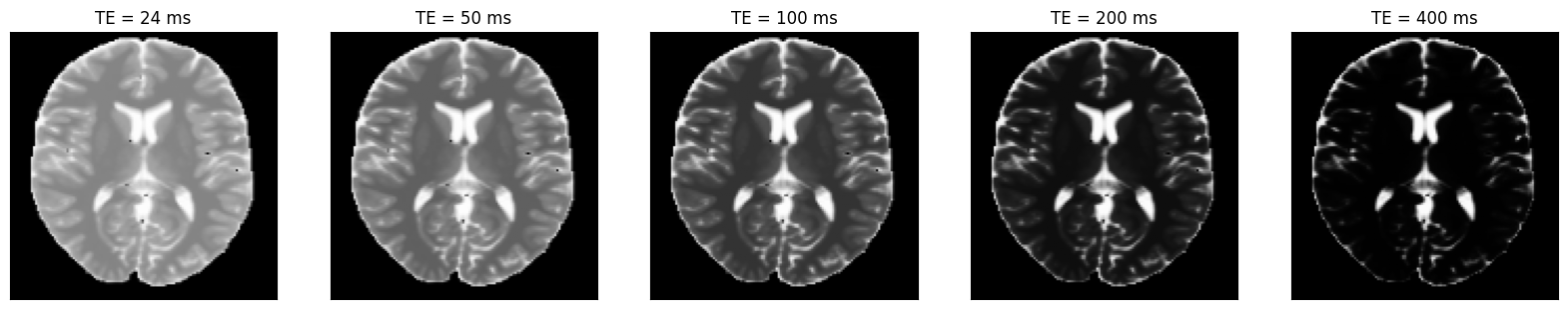
Reconstruct the images at different echo times#
We use MRpro for the image reconstruction.
kdata = KData.from_file(fname_mrd, trajectory=KTrajectoryCartesian())
kdata.header.encoding_matrix = SpatialDimension(z=1, y=image_matrix_size[1], x=image_matrix_size[0])
kdata.header.recon_matrix = SpatialDimension(z=1, y=image_matrix_size[1], x=image_matrix_size[0])
recon = DirectReconstruction(kdata, csm=None)
idata = recon(kdata)
/opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.12.12/x64/lib/python3.12/site-packages/mrpro/data/KData.py:165: UserWarning: No vendor information found. Assuming Siemens time stamp format.
warnings.warn('No vendor information found. Assuming Siemens time stamp format.', stacklevel=1)
We can now plot the images at different inversion times.
idat = idata.data.abs().numpy().squeeze()
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, idat.shape[0], figsize=(4 * idata.shape[0], 4))
for i in range(idat.shape[0]):
ax[i].imshow(idat[i, :, :], cmap='gray')
ax[i].set_title(f'TE = {int(idata.header.te[i] * 1000)} ms')
ax[i].set_xticks([])
ax[i].set_yticks([])
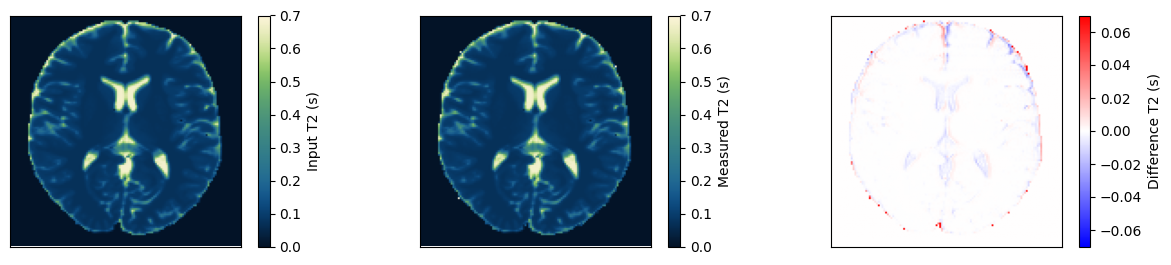
Estimate the T2 maps#
We use a dictionary matching approach to estimate the T2 maps. Afterward, we compare them to the input and ensure they match.
dictionary = DictionaryMatchOp(MonoExponentialDecay(decay_time=idata.header.te), index_of_scaling_parameter=0)
dictionary.append(torch.tensor(1.0), torch.linspace(0.01, 0.8, 1000)[None, :])
m0_match, t2_match = dictionary(idata.data[:, 0, 0])
t2_input = np.roll(rearrange(phantom.T2.numpy().squeeze()[::-1, ::-1], 'x y -> y x'), shift=(1, 1), axis=(0, 1))
obj_mask = np.zeros_like(t2_input)
obj_mask[t2_input > 0] = 1
t2_measured = t2_match.numpy().squeeze() * obj_mask
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(15, 3))
for cax in ax:
cax.set_xticks([])
cax.set_yticks([])
im = ax[0].imshow(t2_input, vmin=0, vmax=0.7, cmap=Colormap('navia').to_mpl())
fig.colorbar(im, ax=ax[0], label='Input T2 (s)')
im = ax[1].imshow(t2_measured, vmin=0, vmax=0.7, cmap=Colormap('navia').to_mpl())
fig.colorbar(im, ax=ax[1], label='Measured T2 (s)')
im = ax[2].imshow(t2_measured - t2_input, vmin=-0.07, vmax=0.07, cmap='bwr')
fig.colorbar(im, ax=ax[2], label='Difference T2 (s)')
relative_error = np.sum(np.abs(t2_input - t2_measured)) / np.sum(np.abs(t2_input))
print(f'Relative error {relative_error}')
assert relative_error < 0.02
Relative error 0.011918182484805584